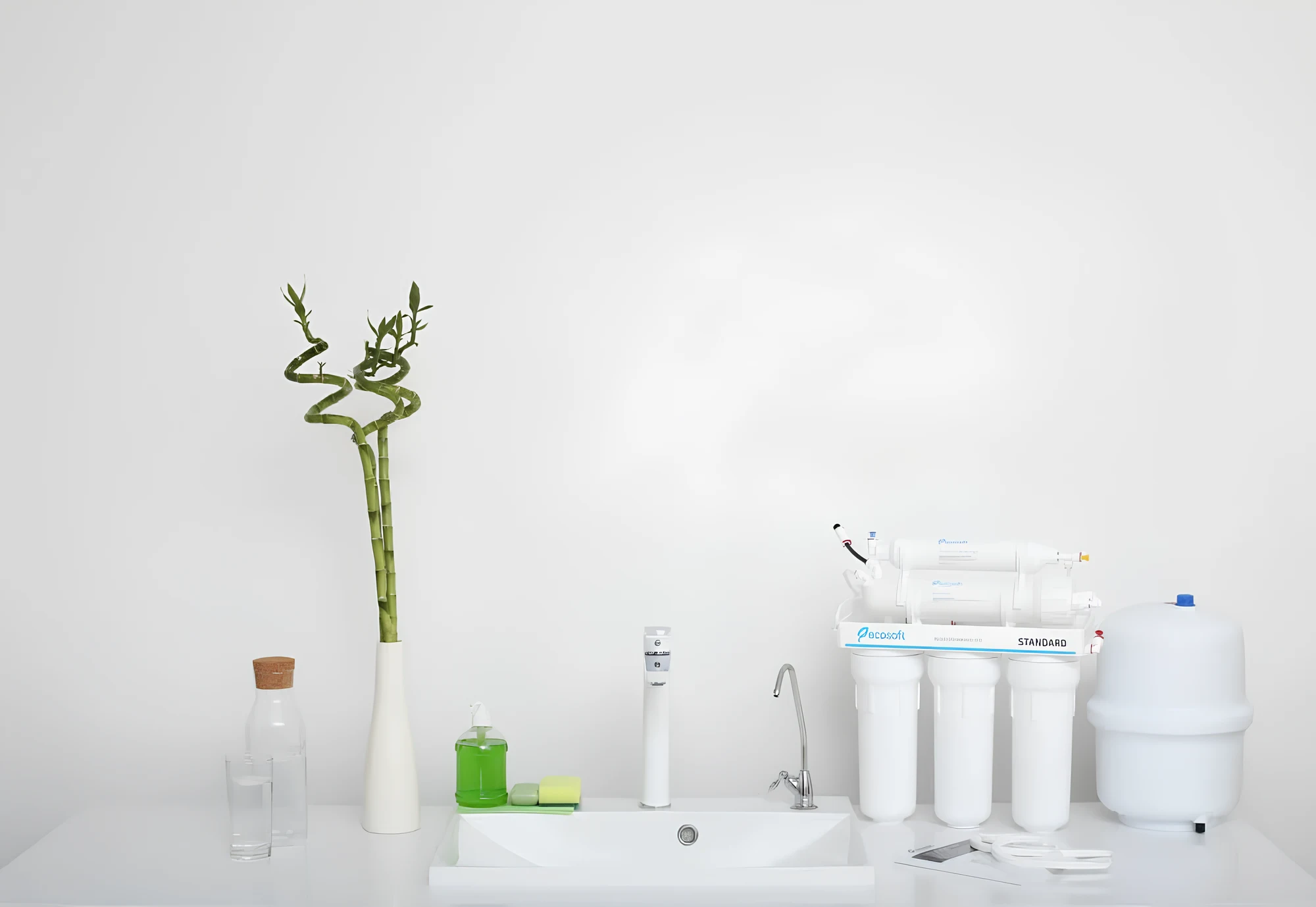
The use of reverse osmosis filters has become essential in many Ukrainian households. However, with their increasing popularity, many questions related to problems with reverse osmosis have arisen about malfunctions in their operation. Let's take a closer look at the reasons for these malfunctions.
What Is Reverse Osmosis Filtration?
Reverse osmosis is a membrane process in which a solvent, typically water, passes through a semi-permeable membrane from a more concentrated solution to a less concentrated solution, in the opposite direction to natural osmosis. This process requires the application of external pressure to overcome the natural osmotic pressure. The membrane permits the solvent to pass through while preventing impurities dissolved in it from passing. This selective permeability is achieved due to the microscopic pores in the membrane that are small enough to block contaminants but allow water molecules to flow through.
Due to the unique properties of reverse osmosis membranes and the physics of the process, reverse osmosis can effectively remove the smallest particles of contaminants, including viruses and metal ions, ensuring high purity of the treated water. The process is highly efficient and can reduce a wide range of contaminants, including dissolved salts, bacteria, and organic compounds. This makes reverse osmosis an essential technology for applications requiring exceptionally clean water, such as in the production of drinking water, pharmaceuticals, and semiconductor manufacturing. Additionally, reverse osmosis systems are widely used in desalination plants to produce fresh water from seawater, providing a critical resource in arid regions and for various industrial processes.
How Does Reverse Osmosis Water Filtration Work?
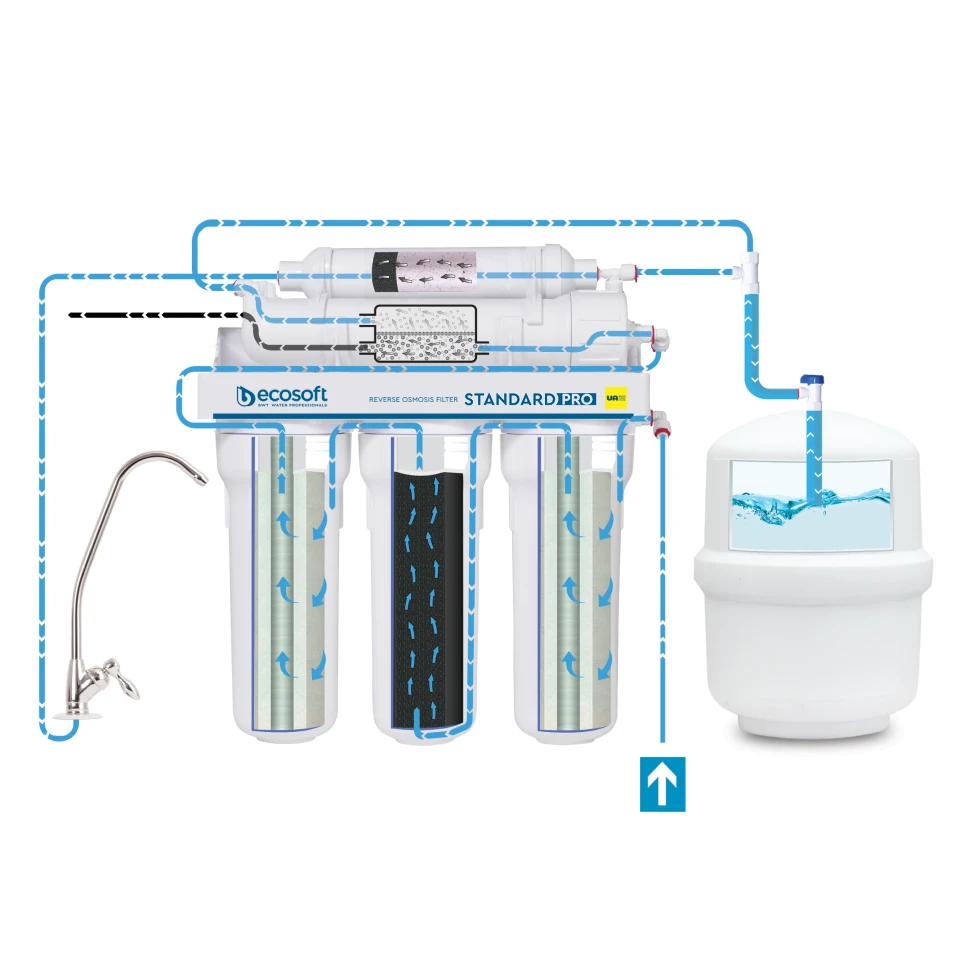
Reverse osmosis water filtration operates by applying pressure to force water molecules through a semi-permeable membrane, which separates contaminants from the water. Initially, feed water containing dissolved impurities is pressurized and directed through the membrane. The semi-permeable membrane has tiny pores that allow only water molecules to pass through, effectively blocking larger particles. This pressure-driven separation is crucial to counteract the natural osmotic pressure and achieve effective purification.
The purified water, now largely free of contaminants, is collected as permeate or product water, while the concentrated reject stream containing the impurities is discharged as brine or waste. Reverse osmosis systems usually consist of several stages, including pre-filtration to remove larger debris and post-filtration to further refine the water quality. The high efficiency of reverse osmosis makes it ideal for various uses, ranging from providing clean drinking water for households to treating industrial wastewater and producing ultra-pure water for medical and technological applications.

Benefits of Reverse Osmosis Water Filtration
Reverse osmosis water filtration offers numerous benefits, making it a preferred choice for both residential and industrial applications. Here are some of the key advantages:
1. Effective Contaminant Removal: Reverse osmosis systems can remove a wide range of contaminants, including dissolved salts, heavy metals, bacteria, viruses, and organic compounds. This ensures exceptionally pure water that is safe for drinking and various industrial processes.
2. Improved Taste and Odor: By eliminating impurities, reverse osmosis significantly enhances the taste, odor, and overall quality of water, making it more palatable for consumption.
3. Energy Efficiency: Compared to other purification methods, reverse osmosis is energy-efficient, especially in large-scale applications such as desalination plants.
4. Low Maintenance: These systems require minimal maintenance and can operate continuously, providing a reliable supply of high-quality water.
Disadvantages of Reverse Osmosis Water Filtration
While reverse osmosis water filtration offers many benefits, it also has some disadvantages that should be considered.
1. Water Wastage: Reverse osmosis systems can produce a significant amount of wastewater, with only a portion of the feed water being converted into purified water. This inefficiency can be a concern, especially in areas with limited water resources.
2. High Initial Cost: The installation of reverse osmosis systems can be expensive, especially for large-scale applications. The cost includes not only the equipment but also the necessary pre-treatment and post-treatment components.
3. Energy Consumption: Although reverse osmosis is relatively energy-efficient compared to other methods, it still requires considerable energy to maintain the high pressure needed for the process. This can lead to higher operational costs.
4. Mineral Removal: Reverse osmosis removes not only harmful contaminants but also essential minerals from the water, such as calcium and magnesium. This can result in water that is less beneficial for human consumption unless remineralization is applied.
Causes of Issues with Reverse Osmosis Filters
Encountering issues with your reverse osmosis water filter not working can be a frustrating ordeal. Exploring the root causes behind these problems is essential for troubleshooting and ensuring the continued functionality of your filtration system. In this discussion, we will delve into common reverse osmosis system problems such as expired service life, low-quality systems, production defects, and operational challenges, offering insights to help you address and prevent osmosis problems effectively.
- Filters can malfunction due to expired service life, worn-out cartridges, hoses, and fittings. The length of the operational life varies between manufacturers, but Ecosoft filters have a service life of five years.
- Low-quality systems can also cause problems. If the price of a system seems too good to be true, it's worth reading reviews before purchasing.
- Production defects can occur with any manufacturer. Malfunctions often occur shortly after purchasing a filter and are usually covered by the manufacturer's warranty.
- Other reverse osmosis troubleshooting can be associated with operation and maintenance. Let's take a closer look at the most common reverse osmosis system problems: water leaks, unpleasant taste, and slow tank filling.
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Low Water Pressure | Clogged filters or membrane | Replace filters and membrane |
| Slow Water Flow | Low feed water pressure or tank pressure is low | Increase feed water pressure or check tank pressure |
| Bad Taste or Odor in Water | Worn-out filters or membrane | Replace filters and membrane |
| Leaking System | Loose connections or damaged tubing | Tighten connections or replace tubing |
| No Water Flow | Clogged filters, membrane, or airlock in system | Replace filters, membrane, and clear airlock |
| High TDS Levels in Output Water | Faulty or old membrane | Replace membrane |
Low Water Pressure in The Reverse Osmosis System

Encountering osmosis water system problems like low water pressure in your RO system can disrupt its efficiency and performance. To address this, we need to understand the root causes of the issue and how to increase water pressure in RO systems. Common factors such as limited water supply, low pressure in the pipeline, untimely replacement of pre-filter cartridges or membrane elements, and low pressure in the accumulation tank can all contribute to this problem.
- Limited water supply
If you have recently installed or serviced your system, check if the pipes are not blocked and the tank valve is fully open. - Low pressure in the pipeline.
If the pressure in your pipeline is below 3 atm, it will be insufficient for the filter to function properly. The tank will fill up very slowly, and a lot of water will be wasted. This problem can be solved by installing a pump. - Untimely replacement of pre-filter cartridges or membrane elements.
After the expiration date or increased water consumption, the membrane element becomes clogged with slime, causing the filter to fill the tank slowly. Untimely replacement of cartridges will result in unfiltered water entering the membrane, which in turn will accelerate its clogging. If you change the membrane and pre-filter cartridges on time, but this happens regularly, we recommend replacing the 1-2-3 set more often. We have written about this in detail before. - Low pressure in the accumulation tank.
The pressure should be 0.4-0.6 atm (bar) under normal conditions. If the pressure is not adequate, it needs to be boosted using a pump. This service has to be provided by the service engineer.
Why My Filter is Leaking?

The occurrence of leaks in a water filter can stem from various osmosis problems. Understanding the root causes behind these leaks is essential before attempting any repairs. Identifying the specific issues contributing to the leakage is crucial for effectively addressing reverse osmosis system problems and ensuring the proper functioning of the filtration system.
Incorrect connection or maintenance
Such malfunctions usually occur immediately after manual manipulation of the system or after the technician's visit. To fix such problems, it is enough to carefully inspect the filter, detect the leakage, and seal the found point. The main places of leakage can be clips on hoses, drainage, and connections between the flask and the base. To fix this problem, you can disconnect the filter, detach and reconnect the connections.
Pressure surges in the system
Most systems have an allowable working pressure of up to 6 atm (bar). If your water supply system has pressure fluctuations, it is recommended to install a pressure reducer to protect the filter. After installing the pressure reducer, it is necessary to check all fittings and connections.
Wear of the sealing gasket between the flask and the head
This happens if the installation has reached the end of its service life, and it is necessary to replace the gasket or call a service engineer to install it.

Mechanical damage
This can happen during transportation or incorrect maintenance or installation.
Poor quality components
This often happens in "no-name" systems. Usually, these problems can be solved by a service center.
To find out why the water filter has burst, it is always necessary to check 2, 4, or 5 factors. Usually, they are the cause of the accident.
High Level of Noise
If your system is making a lot of noise, the cause may be:
- Air in the auto-regulator - this problem will resolve itself after some time.
- High pressure at the system inlet. In this situation, it is recommended to install a check valve at the apartment inlet or directly before the system.
- Low pressure level in the tank.
Why The Reverse Osmosis Pump Won't Turn On?
The pump for reverse osmosis filters is designed to increase pressure directly in front of the filter. It allows to increase the filter's productivity and reduce water discharge into the drain. The reasons why the pump may not be working are:
- Low pressure in the pipeline - each pump has a minimum input pressure indicator, usually 1.5 - 2 atm, if it is lower, the pump will not work;
- Hose clogging, this problem usually occurs immediately after replacing the cartridges;
- Lack of power supply to the pump - check the connection to the network.
Why Is My Reverse Osmosis Tank Not Filling Up?
If your reverse osmosis tank is not filling up, it could be due to several common issues. One potential cause is low water pressure, which can hinder the system's ability to push water through the membrane. Additionally, a clogged or fouled membrane might be restricting water flow, leading to inadequate filling. Other potential problems include a malfunctioning automatic shut-off valve or a leaky tank bladder. To troubleshoot your reverse osmosis water filter system, start by checking the water pressure and inspecting the membrane for any signs of blockage or wear. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of filters and membranes are crucial to ensure your reverse osmosis system works efficiently and resolves osmosis water system problems.
Why Does My Reverse Osmosis System Constantly Drain Into The Drain?
The membrane or cartridge pre-filters may be contaminated. Contamination reduces the filter's capacity or simply clogs it, resulting in the pipeline pressure being unable to push water through the membrane. In such a situation, scheduled maintenance will resolve the issue.
Low pressure at the system's inlet also leads to the inability of liquid to pass through the membrane element, and large volumes of water are discharged into the sewer. The tank slowly fills with water.
Faulty auto-regulator. To check this point, you need to close the tap on the tank. In 2-5 minutes, the auto-regulator should shut off the water supply to the system. If this does not happen, you should contact a service center to replace the auto-regulator.
Malfunction of the membrane's check valve. If this part is broken, even if the tank is full, water continues to flow onto the membrane and bypass it, draining into the sewer.
Low pressure in the tank.
Blocked or faulty flow restrictor. It should be inserted into the black-colored tube on the outlet of the membrane holder. If the part is missing, it is likely that it has been washed away into the sewer and a new element needs to be installed. Also, it may be located near the drain clamp. In that case, it needs to be flushed and the tube installed into the flow restrictor closer to the membrane holder.
Water Is Not Draining Into The Drain
This indicates that the system is not functioning. The cause of this problem may be a blocked flow restrictor that needs to be removed and flushed, or an incorrectly installed drain clamp. In the latter case, you should check the alignment of the openings in the pipe and the installed clamp.
How to Repair a Faucet For a Drinking Water Filter?
Our clients rarely complain about the breakdown of water faucets, which usually occurs after many years of service. If your drinking water faucet has started to leak, we recommend replacing it. However, if you have decided to repair it:
- remove the plug from the faucet valve;
- unscrew the screw with a cross-shaped screwdriver;
- remove the valve from the base of the faucet;
- remove the retaining washer;
- unscrew the screws with pliers;
- remove the faucet sleeve and extract all the parts from it;
- remove the rubbers from the central metal part (rubbers diameter - 6 mm) and replace them;
- clean all parts;
- lubricate the faucet head;
- reassemble the faucet in reverse order.
If these operations do not help, then you will still have to replace the faucet.
Why Does My Reverse Osmosis Water Taste Bad?

If you notice an unusual odor or taste in your water, it may be due to an exhausted carbon post-filter. Over time, the carbon filter loses its ability to effectively remove contaminants and impurities, leading to reverse osmosis problems. In this case, simply replace the filter to solve the issue and restore the water's taste and quality. Regular replacement of the carbon filter is an essential part of maintaining your RO system and preventing water filter osmosis reverse problems.
Another possible cause of bad-tasting water is contamination of the system or tank, which often results from incorrect maintenance. Contaminants can accumulate in the system if it is not regularly cleaned and disinfected, leading to osmosis water system problems. To prevent this, regular service and disinfection of the system are necessary. Thoroughly clean and sanitize the RO system and storage tank at least once a year to ensure the removal of any built-up bacteria or other contaminants.
For effective RO system troubleshooting, check all components for potential issues. Ensure that all filters are replaced according to the manufacturer's recommendations, and inspect the membrane for any signs of fouling or damage. Regular maintenance and prompt attention to any abnormalities are key to resolving reverse osmosis not working issues and ensuring your water tastes fresh and clean. If the problem persists despite these measures, it may be beneficial to consult a professional for comprehensive reverse osmosis system troubleshooting.
Alternatives to Reverse Osmosis Water Filtration
Several alternatives to reverse osmosis water filtration exist, each with its own advantages and applications. Activated carbon filters are widely used to remove chlorine, organic compounds, and improve taste and odor, making them ideal for point-of-use filtration. Ultraviolet (UV) purification systems effectively disinfect water by inactivating bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens without adding chemicals. Ion exchange systems are another option, primarily used for water softening by replacing calcium and magnesium ions with sodium or potassium ions. Additionally, ceramic filters can remove bacteria and protozoa, making them suitable for both household and portable water purification. These alternatives offer diverse solutions for achieving clean and safe water depending on specific needs and contexts.
Turbidity After Purification
This occurs because the water is saturated with air. It is not indicative of a malfunction and will usually pass within one or two weeks after installing the filter. To confirm whether it is air, pour water into a glass and let it sit for 5–10 minutes.
It is important to note that this can happen in winter when the temperature difference between the water and the environment is significant.
If you encounter any issues not listed here, please let us know in the comments.
And remember, at Ecosoft, you can not only purchase high-quality filters but also receive exceptional customer service.
Faqs
Why is my reverse osmosis system producing less water than before?
There could be several reasons why your reverse osmosis system is producing less water than before. Firstly, check if the water pressure in your home has decreased. Low water pressure can directly affect the production rate of your system. Additionally, a clogged pre-filter or sediment filter can restrict water flow and reduce production. It is recommended to inspect and clean or replace these filters regularly. Another potential cause could be a malfunctioning or worn-out membrane. Over time, the membrane may degrade or become damaged, resulting in decreased water production. If none of these solutions solve the issue, it is advisable to consult a professional for further assistance.