A few days ago, there was a question in the comments section of our website asking whether a mineralizer can change the oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) of water. Since this parameter is not a quality indicator for water in Ukraine and is used in completely different processes unrelated to drinking water treatment, we decided to investigate the origin of this question.
If you “Google” it, the first results about negative ORP in water describe it as a determinant of "living" and "dead" water. Since we live in an era of high-quality analytical chemistry and evidence-based medicine, such materials raise skepticism.
Therefore, we decided to look for confirmation or refutation of the healing properties of such water in scientific literature. This article will cover what we knew and what we found in scientific databases.
Regulatory values
First, let's examine the national and international standards for drinking water.
This parameter is not regulated because it does not define any actual quality indicators for water. It is absent in the State Sanitary Rules and Regulations (DSanPiN 2.2.4-171-10), which govern drinking water quality in Ukraine, and in the documents of the World Health Organization (WHO), as well as in drinking water standards of European countries.
In WHO documents, which describe the assessment of water quality, the redox potential (another name for ORP) is described exclusively as a parameter that determines the effectiveness of chlorine as a disinfectant and as a preliminary evaluation of the likelihood of certain pollutants being present in the water.
What does the ORP of water mean?
Oxidation-reduction potential (reduction-oxidation reaction) or redox potential characterizes the ability of a substance to attach ions or undergo reduction.
Water always contains certain substances that are oxidizers and reducers. These substances form oxidation-reduction pairs that exchange electrons. They carry a negative charge (one electron removes one unit of charge from an atom).
For example, hydrogen sulfide is a reducer — a substance whose atoms can donate electrons.
Hydrogen peroxide, on the other hand, is an oxidizer — a substance whose atoms can accept electrons.
In the course of a reaction, the charge of the oxidizing atoms decreases because the added electrons have a negative charge, while the charge of the reducing atoms increases because they donate negatively charged electrons. The pair formed by the donor and acceptor is called an oxidation-reduction pair.
The relationship between ORP and pH
If the oxidizers in the pair contain oxygen (for example, Cr2O72-, CrO42-, MnO4-), the oxidation potential increases as the concentration of H+ ions (a decrease in pH) increases. If the concentration of OH- ions increases (a rise in pH), the potential decreases. This means that the higher the pH, the lower the potential.
The concentration of the reducer or oxidizer also plays a role. In this case, using a water ionizer will indeed lower the ORP along with a decrease in pH. We have already written about how an ionizer works in earlier materials.
What does the magnitude and sign of ORP indicate?
This value allows predicting whether the solution will have oxidizing or reducing properties. The higher the ORP value of a pair, the higher its oxidizing potential, and vice versa.
Virtually all processes that occur in water have a negative potential. As a result, without the addition of foreign substances, the question will only concern the concentration of ions.
Why do reactions not occur continuously?
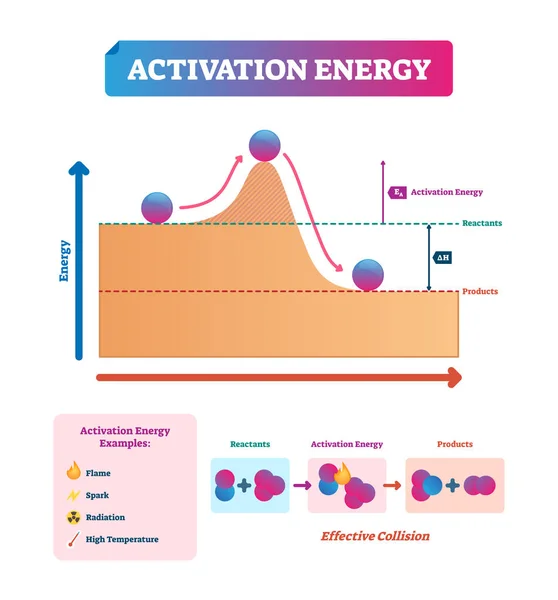
This is a very important question. In reality, certain processes constantly occur in water, but not all of them. For example, metallic calcium or sodium do not precipitate from water under normal conditions, nor does hydrogen release, even though, based on the potential values, these reactions are possible.
Even if the potential is high (whether negative or positive), a reaction may not necessarily occur. The image here shows a ball standing on a slope but not moving. For it to start moving, it needs a push, called activation energy. If the necessary activation energy is too high, the reaction may never take place. Most of the likely reactions that can be predicted do not occur in water or biological environments.
It is also important to remember that water itself has a negative redox potential. For example, this can be reduced with molecular hydrogen or ascorbic acid solutions, as well as with heavy metal ions like aluminum. Therefore, it is crucial to carry out any manipulations only with clean water.
How does an ORP meter work?

The oxidation-reduction potential of water, like that of any other solution, is measured using a special device. In fact, an ORP meter is a potentiometer or voltmeter. It measures the electromotive force caused by the electrons moving from the reducing substance to the oxidizing substance.
Measurement is carried out using a special electrode with a sensor and converter that displays the readings on the screen.
The unit of measurement for ORP is mV (millivolts).
Evidence base
Scientists have determined that the ORP of all liquid environments in the human body will always be negative. Therefore, some researchers allow the possibility that consuming liquids with a negative (reducing) potential could have a positive effect on health.
However, we were unable to find clinical studies confirming the effectiveness of such water in improving well-being. Most publications are related to laboratory experiments or methods of obtaining water. Some of the studies were conducted for marketing purposes by certain water ionizer manufacturers.
It is also important to note that liquids from fresh vegetables and fruits have a negative potential, while prepared food products, beverages, and tap water have positive potential values.
Natural waters also very rarely have a negative potential, such as waters obtained from mountain glacial springs.
Conclusions
The oxidation-reduction potential is not a regulated parameter for water quality, so it is not advisable to assess the water you consume based on its value.
The benefits or harms of water with a low or high ORP for human health are not proven.
Both safe substances and potential toxins can influence the redox potential of water.








